Technical cooperation in the field of statistics refers to capacity building activities of the EFTA Secretariat, implemented together with the four EFTA States, in EFTA partner countries in neighbouring regions to the EU and the EEA. In close cooperation with the EFTA States, and in coordination with Eurostat and other international partners such as UNECE, the EFTA Secretariate provides support to these partner countries to develop their statistical capacity and to harmonise official statistics with European methods and standards because this supports economic cooperation and integration, which ultimately fosters sustainable prosperity, peace and a better quality of life in partner countries.
Technical cooperation in the field of statistics includes the following regions and countries:
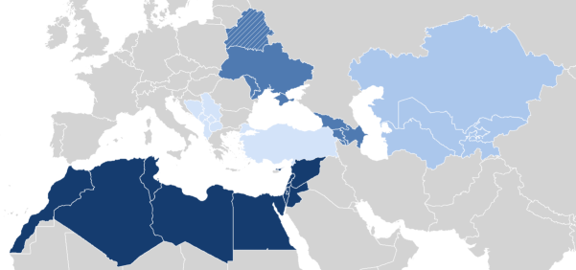
EU Candidate and potential candidate countries: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Kosovo, Moldova, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Türkiye and Ukraine.
EU Neighbourhood Policy South: Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Libya, Morocco, Palestinian Authority, Syria, and Tunisia.
EU Neighbourhood Policy East: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus*, Georgia, Moldova, and Ukraine.
Central Asia countries: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan.
EFTA free trade partners and prospective free trade partners.
*Following the military aggression by Russia and Belarus against Ukraine in February 2022, EFTA has withdrawn from all cooperation activities with Russia and Belarus. The technical cooperation is thus limited to the EFTA partner countries, i.e. all of the above excluding Belarus.
The EFTA Secretariat implements the technical cooperation activities based on an Administrative Arrangement between the EFTA Secretariat and the European Commission (Eurostat) and annual technical cooperation programmes as approved by the EFTA Council. These statistical capacity building activities are implemented through the following actions:
- Seconded National Experts (SNEs): Up to two SNEs from the National Statistical Institutes of the EFTA States are seconded to Eurostat’s statistical cooperation unit. The SNEs work directly with programming and implementation of the Eurostat’s capacity building activities in the field of statistics.
- Statistical Assessments: Statistical assessments include Global Assessments, Peer Reviews and Sector Reviews. Global Assessments are screenings of National Statistical Institutes and of the National Statistical Systems with an emphasis on legal and institutional and institutional environment towards implementation of the European Statistics Code of Practice (ESCOP), the UN Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics, and international statistical standards for statistical domains. Peer Reviews focus mainly on the institutional and legal aspects with the ESCOP as benchmark. Sector Reviews are assessments related to a specific statistical or technical field with the EU acquis as benchmark. Such statistical assessments identify areas for developing and aligning the functioning and institutional framework of the statistical systems in partner countries with European and global standards. The assessments can therefore be instrumental to developing the national statistical systems in partner countries. They can also be used to derive further technical cooperation needs of the partner countries.
- Workshops, conferences or trainings: The EFTA Secretariat organises workshops, conferences and trainings in various fields of statistical production methodologies for staff of National Statistical Institutes of partner countries, usually with the expertise from the EFTA States, and in cooperation with Eurostat and UNECE. The aim is to transfer knowledge to various staff (senior management as well as statistical officers in different domains) in National Statistical Institutes of EFTA partner countries, on strategic issues and implementation of statistical methods and standards.
- Support to development of specific statistical areas in the partner countries: The EFTA Secretariat also supports development of specific statistical domains in EFTA partner countries, by organising expert missions from the EFTA States to work together with the partner countries on implementing European standards and methodology in specific statistical domains.